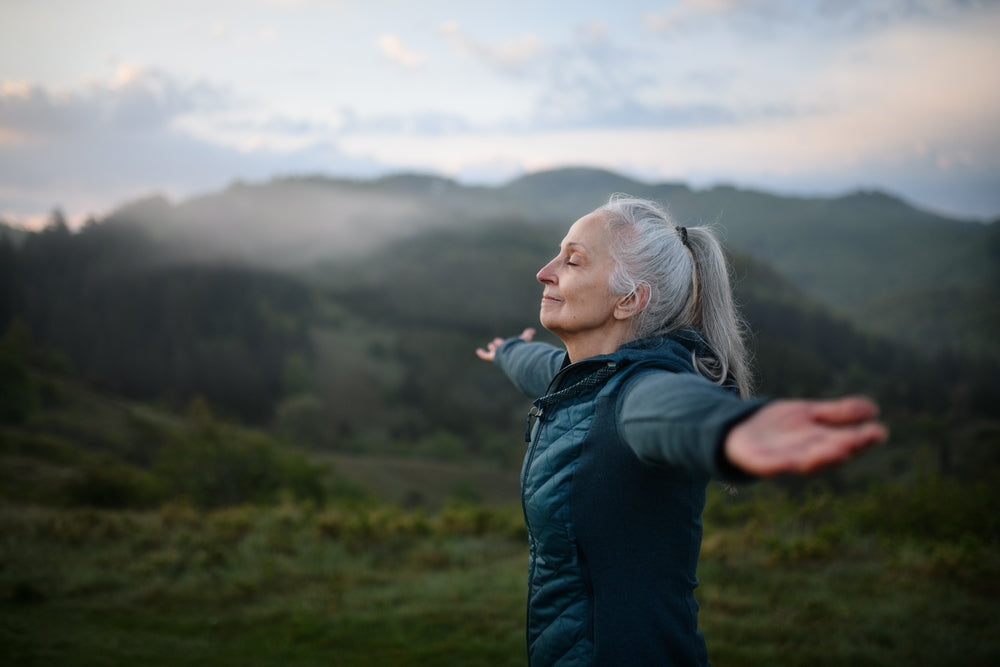
In the pursuit of well-being, exploring innovative methods to enhance both physical and mental health is key. One such avenue gaining traction is vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), a technique that holds promise in regulating various bodily functions and promoting overall wellness.
Understanding the Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, is a vital component of the autonomic nervous system, responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. It serves as a bridge between the brain and several organs throughout the body, exerting profound influence on overall health.
Benefits of Vagus Nerve Stimulation
1. Stress Reduction and Mental Well-Being
VNS has shown promise in alleviating stress, anxiety, and depression by modulating the body's stress response system. By activating the parasympathetic nervous system, VNS promotes relaxation and emotional balance, offering a natural and non-pharmaceutical approach to mental health management.
2. Improved Heart Health
Through its influence on heart rate variability and cardiac function, vagus nerve stimulation can support cardiovascular health. Studies have suggested that VNS may help regulate blood pressure, reduce arrhythmias, and enhance heart rate control, offering potential benefits for individuals with heart conditions.
3. Enhanced Digestive Function
The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in gastrointestinal function, influencing digestion, nutrient absorption, and gut-brain communication. VNS has shown promise in managing digestive disorders such as gastroparesis and inflammatory bowel disease, highlighting its potential to optimize digestive health.
4. Pain Management
Chronic pain conditions can significantly impact quality of life, and VNS offers a non-pharmaceutical approach to pain management. By modulating pain perception pathways and releasing endogenous opioids, VNS may provide relief for individuals suffering from conditions such as migraines, fibromyalgia, or neuropathic pain.
Ways to Stimulate the Vagus Nerve
1. Deep Breathing Exercises
Engaging in slow, deep breathing activates the relaxation response mediated by the vagus nerve. Practice diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, by inhaling deeply through your nose, allowing your abdomen to expand, and exhaling slowly through your mouth.
2. Meditation and Mindfulness
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and guided imagery, can stimulate the vagus nerve and promote relaxation. Focus on the present moment, cultivate gratitude, and observe sensations in your body to activate the parasympathetic nervous system.
3. Yoga
Certain yoga poses, particularly those that involve gentle stretching and deep breathing, can stimulate the vagus nerve. Practices like cat-cow pose, cobra pose, and child's pose may help activate the relaxation response and improve vagal tone.
4. Cold Exposure
Exposure to cold temperatures, such as cold showers or cold water immersion, can activate the vagus nerve's response, known as the "diving reflex." Brief exposure to cold stimulates the body's adaptive stress response and may enhance vagal tone over time.
5. Singing or Chanting
Vocal exercises, singing, or chanting can stimulate the vagus nerve by engaging the muscles in the throat and vocal cords. Singing hymns, chanting mantras, or practicing vocal exercises may help enhance vagal tone and promote relaxation.
6. Laughter and Social Connection
Laughter stimulates the vagus nerve and releases endorphins, promoting feelings of well-being and relaxation. Spend time with loved ones, engage in activities that bring joy and laughter, and cultivate meaningful social connections to support vagal activation.
7. Massage and Acupressure
Gentle massage or acupressure techniques targeting specific areas of the body, such as the neck, ears, or feet, can stimulate the vagus nerve indirectly. Explore self-massage techniques or seek professional massage therapy to promote relaxation and vagal activation.
8. Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting or time-restricted eating patterns may promote vagus nerve function by supporting metabolic flexibility and autophagy. Consult with a healthcare professional before initiating any fasting regimen to ensure it aligns with your individual health needs.